Bradycardia: Artificial
Pacemaker
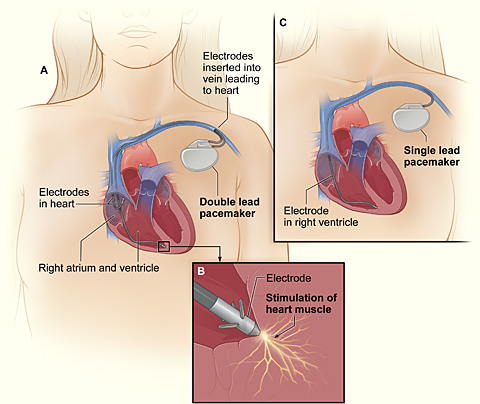 |
| figure 1. Artificial Pacemaker placement |
For
bradycardia patients, doctors usually hold off any medications that slows their
heartbeat, and treat the conditions by implanting a permanent or temporary
pacemaker (Arrhythmia Alliance, 2012). An artificial
pacemaker is a small battery operated device, that is approximately the size of
a fifty pence piece, used to detect and fires a small electrical impulse to
stimulate the heart wall to make it contract and to make the heart beats. It is
planted just under the skin of your chest (below your collar bone) and
insulated lead wires that connects to the pacemaker are attached to the heart
to help your heart muscle pump blood regularly (National
Heart Foundation Australia, 2015;Adelaide-Meath National Children's Hospital,
2015) . The lead also provides the information on the heartbeat’s
natural activity. The body will not reject artificial pacemaker.
Tachycardia: Vagal Maneuvers,
Cardioversion, Catheter Ablation and Pharmacological Medications
Vagal maneuver is a set of physical activities that stimulate the Vagus
nerve, the nerve serving
the structures of the chest, abdomen, head and neck, which supplies
parasympathetic impulses to the myocardium (heart muscle) and trigger the release of acetylcholine to put halt on the conduction of electrical impulses and decrease
the rapidity of the heart (Healthwise
Staff, 2012;Wang & Estes, 2014). The
maneuvers are gagging, holding your breath and bearing down (Valsalva
maneuver), immersing your face in ice-cold water (diving reflex), coughing and
Carotid massage (neck massage).  |
| figure 2. Cardioversion |
Cardioversion uses electrode patches to deliver a split-second energetic
shock to the heart muscles while the patient is sleeping, the shock applied
will interrupt the abnormal heart rhythm and return a normal heartbeat (Intermountain Healthcare, 2011;Texas Cardiac
Arrhythmia Institute, 2015;Tandri, 2015). This quick procedure may need
to be repeated to effectively restore a normal heart rhythm under the direction
of a team of highly trained doctors, nurses and technologists in the
electrophysiology lab (Intermountain Healthcare, 2011).
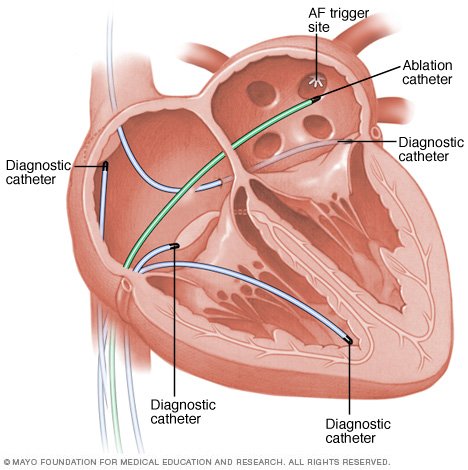 |
| figure 3. Catheter Ablation |
Catheter ablation uses radiofrequency energy to destroy (ablate) a small area of
the tissue of the heart which is causing arrhythmia. Guided with x-rays, the
doctor will insert several small catheters (thin, flexible tubes) through the
veins in the groin or neck and direct them to the tissues that interrupt the
heart’s electrical activity then thermal energy (extreme heat) or cryoenergy
(extreme cold) energy will be emitted to the problematic tissues through one of
the catheters (National Institute of Health,
2012;American Heart Association, 2014;Cleveland Clinic, 2015;Ashikaga, 2015).
This energy also disconnects the electrical pathway of the abnormal rhythm.
There are three main pharmacological drugs being prescribed
to an arrhythmic patient, they are the anti-arrhythmic drugs, the calcium
channel blockers and beta-blockers (American
Heart Association, 2014;Healthline Networks, 2015). Anti-arrhythmic drugs either cease the abnormal transmission of
electrical impulses send by the natural pacemaker tissue that is firing too
fast to the heart tissues (American Heart Association, 2014). The drugs are in a
form of pills or in a form of intravenous (IV) drip, they work to correct and
restore the normal rhythm of the heart. Next is the calcium channel blockers, which is also known as "calcium
antagonists." Calcium is an electrolyte that functions as the heart
regulator, imbalance of calcium will cause arrhythmia. Thus, calcium channel
blockers work by blocking the movement of the calcium electrolytes into the
heart and blood vessel tissue (Healthline Networks, 2015). It can be taken in
a form of pill or in a form of intravenous (IV) drip. Lastly,
beta-blockers, which is also known as ‘beta-adrenoceptor blocking’ that blocks adrenaline hormones from
stimulating rapid firing of electrical impulses to the heart tissues,
thus results in a decrease of heart beats, reduction of cardiac stress output
and lessening of the arterial blood pressure (Healthline Networks, 2015).
Bradycardia and
Tachycardia: Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD) and Surgeries
| figure 4. ICD |
Two of the main surgeries for treating arrhythmia are the maze procedures and
coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery (University of California San
Francisco, 2015).
Maze surgery treats arrhythmia by making small cuts or burns in the heart tissues
that will prevent the transmission of abnormal electrical signals or by making
a "maze" of new electrical routes to let electrical impulses move
easily to the heart tissues (Texas Heart
Institue, 2015;University of California San Francisco, 2015). CABG is
when a healthy artery or vein is extracted from other parts of the body grafted
in between the blocked coronary artery, thus creating a new route for blood to
move to the heart tissues (National Institute of Health,
2012).
Adherence to Medical Advices and Preventive Measures
The most important
part that an arrhythmic patient needs to adhere is to follow the timeliness of
the medicated drug prescribed and to check the functionality of the planted
devices if they previously underwent those procedures. This is to prevent
arrhythmia to advance into a heart attack or a stroke.
As for the medication,
the patient can monitor their consumption by relying to the device called Medication Event Monitoring System (MEMS).
MEMS is a tracking medication usage device without any active patient input. It
consists of an electronic memory integrated into a cap designed to fit a normal
medicine bottle, it records the number of act on when the cap is opened to
remove a pill (Brannon & Feist, 2014).
The health belief model can also be applied,
from the previous consultations with the doctors; patients should already know
the fact that they are susceptible
in getting a heart attack or stroke as they are already arrhythmic. With that
they will come to acknowledge the severity
of getting a heart attack or stroke. Following that, they would search and take
the initiative to know more on how to improve their conditions and to maintain
it that way, in which it is their way of perceiving the benefits of health-enhancing behavior. Lastly, knowing their limits
for the level of exercising or kinds of foods that they can eat without
reaching the excess point is their way of perceiving barriers towards the health-enhancing behaviors (Brannon &
Feist, 2014).
For example, exercising too much may cause their heart to beat faster than
usual or eating too much omega-3 rich foods may cause electrolyte imbalance.


0 comments:
Post a Comment