Arrhythmia divided into
two categories which is the ventricular arrhythmia and supraventricular
arrhythmia, (Texas Heart Institute,2015). The ventricular arrhythmia take place
in the lower chambers of heart termed the ventricles. Meanwhile,
supraventricular arrhythmia take place in the area above the ventricles termed
the atria. The Bradycardia means that the heart beats is too slow and the
Tachycardia means that the heart beats too fast.
Bradycardia
| figure 1. Bradycardia |
Bradycardia is a slow
heart beat which is less than sixty beats per minute. This condition occurs
when the electrical impulse that signals the heart to contract is not formed in
the heart’s natural pacemaker which is the sinoatrial node, or it is not sent
to the ventricles, (University Hospital Southampton,2015). This type of
arrhythmia usually affects elderly people, but there are chances to affect
young generations as well. This condition is caused by any one of two factors
which is the central nervous system does not signal that the heart requires to
pump more or it could be due to the damage of sinoatrial node. The damage of
sinoatrial damage could be associated to aging, congenital defects, heart
diseases or medicines that is taken to control high blood pressure and
arrhythmia.
Tachycardia
Tachycardia is a fast
heart beat which is more than 100 beats per minute. There are few types of
tachycardia which depends on where the fast heart beat originates, (Mayo
Clinic, 2015). If the fast heart beat originates in the ventricles, it is
called the ventricular tachycardia. Meanwhile, if the fast heart beat
originates above the ventricles, it is called the supraventricular tachycardia.
Ventricular Arrhythmias
In ventricular
arrhythmias it consists of Ventricular Tachycardia, Ventricular Fibrillation,
and Premature Ventricular Contractions, (Texas Heart Institution, 2015). . The
ventricular tachycardia is a state in which the sinoatrial node no longer
controls the pounding of the ventricles and the pacemaker’s role is being taken
by the other parts alongside the lower electrical pathway. Since the signal
does not move through your heart muscle along the usual route and this
condition causes the heart muscle does not beat normally. Thus, this condition
would make a person feel as if their heart skip beats and this rhythm cause
severe shortness of breath, syncope or fainting.
Ventricular Fibrillation
| figure 3. Ventricular Fibrillation |
The most serious type of
arrhythmia which results from an uncontrolled and irregular beat. A person who
suffers from ventricular fibrillation would have numerous impulses that arise
at the same time from various locations, (American Heart Association,n.d.). The
heartbeat sometimes could reach about 300 beats per minute and may face chaotic
heartbeat which means a very little amount of blood is being pumped from the
heart to the brain and body and might result in collapsing. Apart from that,
individuals who have history of heart attack or heart disease have a high risk
of getting ventricular fibrillation.
Premature Ventricular
Contractions
Premature Ventricular
Contractions also known as Premature Ventricular Beat is a less serious sort of
ventricular arrhythmia. According to Kulick and at el. (2015), this condition
occurs when ventricles contract rapidly out of order with the regular
heartbeat. Normally there is no treatment is needed for this condition but if
the individual have a history ventricular tachycardia or heart disease, it might cause
a serious type of arrhythmia. This condition could be caused by caffeine and
over-the-counter cold and cough medicine.
Supraventricular
Arrhythmias
In supraventricular
arrhythmias it consists of Supraventricular Tachycardia also known as
Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia, Atrial Fibrillation,
Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome, and Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome,
(Texas Heart Institution, 2015). The supraventricular arrhythmia is a state
where it originates in the locations above the heart’s lower chambers which is
the atria or the atrial condition pathways. This condition, may or may not need
treatments and it might be caused by caffeine, alcohol, tobacco or cold and
cough medicines. Moreover, this condition would symptoms such as heart
palpitations, shortness of breath, chest tightness and a very fast pulse rate.
Supraventricular
Tachycardia or Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia
| figure 4. Supraventricular Tachycardia |
The supraventricular
tachycardia is a condition where regular and rapid heart rate from 150 to 250
beats per minute which beats in the atria. Meanwhile, in the paroxysmal
supraventricular tachycardia the word paroxysmal means irregularly or from time
to time. This condition occurs when the electrical signals in the heart’s upper
chambers fire peculiarly, which interferes with the electrical signals that
comes from the sinoatrial node and the beats in the atria eventually speeds up
the heart rate, (John Hopkins Medicine, n.d.). This condition normally common
among infants, young people and most likely to happen in anxious youngsters,
women and individuals who are very worn-out. Other than that, chain smokers,
alcoholic and individuals who takes coffee regularly have a higher risk.
The atrial fibrillation
is a fast and irregular rhythm in which single muscle fibers in heart contract
or twitch, (National Health Service, 2015). This condition might cause the
blood to pool in the heart’s upper chambers and the pooled blood could lead to
blood clot. Once the blood clot travels from the heart and blocks the smaller
artery in the brain, stroke might take place. Thus, when an individual with
atrial fibrillation suffers from stroke, they may need antiplatelet therapy
which could prevent the formation of blood clot and causes stroke.
Wolff-Parkinson-White-Syndrome
The
Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome is a cluster of abnormalities caused by
additional muscle pathways amid the ventricles and the atria, (John Hopkins
Medicine,n.d.). This pathways cause the electrical signals to reach at the
ventricles too quickly, and the signals are sent back to the atria. Thus, it
resulted a very fast heart rate. Individuals with this syndrome might have
symptoms such as dizziness, episodes of fainting, chest palpitations and they
are most likely to have episodes of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia.
 |
| figure 6. Woff-Parkinson-White-Syndrome pathway |
Postural orthostatic
tachycardia syndrome
Generally, when an
individual stands up, the body makes any desirable changes to compensate for
the gravitational stress of adjustment in body posture, (Dysautonomia
International, 2012). In order to keep the oxygen-rich blood flow to the brain
and the upper body, the heart rate increases and the blood vessels in the lower
part of body tighten. For some individuals, this does not occur and affect
their capability to stand or continue standing. This is called the orthostatic
intolerance. The postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome is a type of
orthostatic intolerance. The patients with this condition, the blood vessels in
the lower body do not tighten when they are standing because
 |
| figure 7. Effect of POTS to the body |
of the gravity causes
more blood to flow than normal moves to the lower body. Individuals with this
condition may have symptoms such as blurry vision, fatigue, headaches,
lightheadedness and fainting.
Heart Block
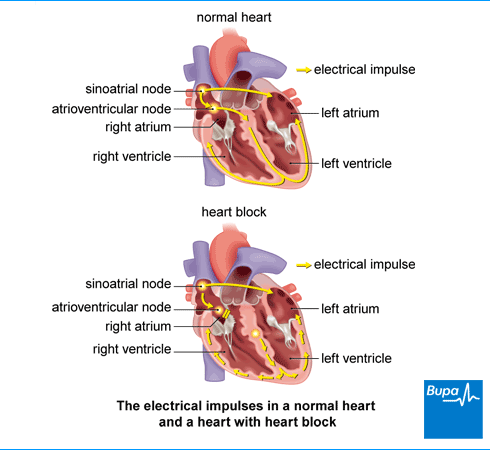 |
| figure 8. Heart Block |
The Heart block occurs
when the sinoatrial node sends its electrical signal appropriately, but the
signal is not sent via the atrioventricular, (Texas Heart Institute,2015). The
condition is most likely caused by aging or by the scarring or swelling of the
heart which at times results from the coronary artery disease. Moreover, it
could be caused by the cardiac amyloidosis, that is a condition where the
amyloid deposits take of the regular heart muscle.
According to National Health
Service (2014), there are few types of heart block, and named according to the
degree of severity.
First-Degree Heart
Block.
The first-degree heart
block means that the impulses are travelling via the atrioventricular node too
slowly.
| figure 9. First-Degree Heart Block |
Second-Degree Heart
Block
The second-degree heart
block means that the impulses are moving via the heart's atria but are deferred
in the atrioventricular node. Due to this delay the ventricles do not beat at
the right time.
Third-Degree Heart Block
The third-degree heart
block means that no impulses are reaching to the ventricles. In order to
make-up for this, the ventricles use its own backup pacemaker by way of its
slower rate. As a gap
in time is probable to
happen among the impulse from the atria and the impulse from the backup
pacemaker in the ventricles, an individual might faint. This situation is known
as a Stokes-Adams attack. The third-degree heart block is very severe and could
lead to heart failure or death.

0 comments:
Post a Comment